Blood Hemolyzing Effects on Laboratory Analytes Explained
In laboratory testing, precision is paramount, and blood hemolyzing remains a significant disruptor. Hemolysis, the rupture of red blood cells that releases hemoglobin and other intracellular components, poses a notable challenge in clinical labs worldwide. When blood hemolyzing occurs, it can severely skew test outcomes, causing inaccurate readings that may lead to misdiagnosis or inappropriate treatment decisions. Understanding how hemolysis affects laboratory analyses is crucial for medical professionals who need to deliver reliable results. Knowing the impacts and causes of hemolysis helps teams mitigate its effects and protect the accuracy of laboratory diagnostics. This blog delves into the essence of hemolysis, identifies factors that contribute to blood hemolyzing, explains its influence on key analytes, and reviews strategies laboratories use to minimize disruption, ultimately supporting more reliable healthcare solutions.
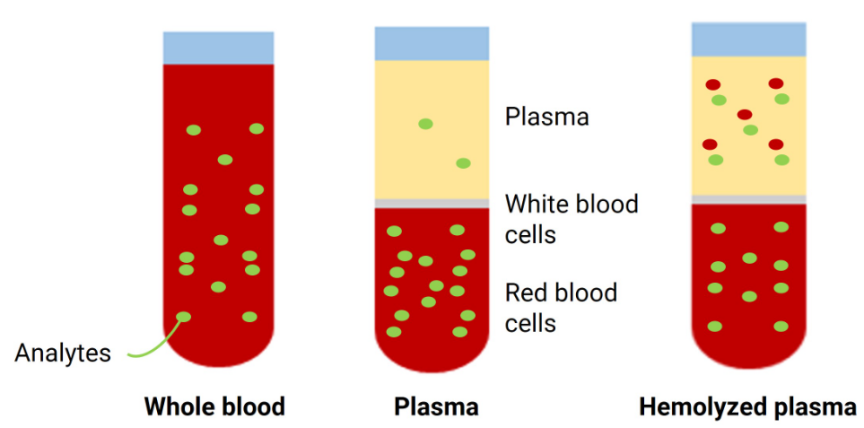
What is hemolysis and why it matters in laboratory testing
Hemolysis occurs when the membrane of red blood cells ruptures, releasing hemoglobin and other cellular components into the surrounding fluid. This process can transpire during or after blood sample collection and handling, posing substantial challenges in laboratory settings. Hemolysis is critical in laboratory testing because it can significantly alter the concentrations of various analytes, leading to erroneous results that can affect clinical interpretations.The presence of free hemoglobin in a sample can interfere with spectrophotometric assays and cause hemoglobin and other intracellular substances to spuriously elevate measured levels of specific analytes. This interference not only impacts the assay’s accuracy but could also mask or mimic pathological results. Medical decisions often rely heavily on lab results; thus, understanding and controlling hemolysis is crucial for ensuring patient safety and effective health management. Accurately identifying hemolyzed samples and comprehending its impacts aids labs in providing clear, actionable insights while reducing potential diagnostic errors linked to compromised blood samples.
Causes of hemolysis in blood samples
Pre-analytical factors during collection and handling
During blood sample collection and handling, pre-analytical factors play a pivotal role in the risk of hemolysis. Improper venipuncture technique, such as using a needle that’s too small or incorrect angle and depth, leads to high shear stress on erythrocytes, resulting in cell rupture. Forceful syringe extraction can similarly create turbulence, facilitating hemolysis. Additionally, inadequate mixing or excessive agitation of blood samples post-collection can disrupt red cells. The use of unsuitable containers or anticoagulants can further contribute to hemolysis, affecting the integrity of the sample. Times between collection and processing also matter; prolonged transport or storage of specimens can increase hemolytic activity if not adequately refrigerated or handled carefully, underscoring the need for stringent handling protocols.
Analytical and biological contributors to hemolysis
Analytical methods and biological factors are equally impactful in initiating hemolysis. For instance, certain automated analyzers may inadvertently cause cell lysis during sample processing due to improper calibration or unsuitable assay setup. Biological contributors, such as hyperlipidemia or pathological conditions like hemolytic anemia, also elevate the natural propensity for red cell rupture. Disease states causing inherent cell membrane instability, and environmental factors such as extreme temperature exposures, can compound these effects, realizing clinically significant hemolysis. Such variability highlights the necessity for adjusted analytical approaches, emphasizing the need for vigilance and informed interpretations of test results amid potential hemolytic interference.
How hemolysis affects key laboratory analytes
Analytes increased due to cell rupture
When red blood cells break down, intracellular contents, such as potassium, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), are released into the plasma. Potassium levels often display marked increases, misleadingly indicating hyperkalemia. Elevated LDH and AST further complicate diagnoses, potentially suggesting tissue damage or cellular necrosis. Hemolysis-induced spikes in these analytes can confound results, leading to unnecessary follow-up testing or inappropriate medical interventions, reinforcing the importance of recognizing hemolysis-driven bias in laboratory analytics to ensure clinical accuracy.
Analytes decreased or distorted by hemolysis
Conversely, hemolysis can result in the apparent reduction or distortion of certain analytes. Bilirubin, crucial in liver function tests, may appear falsely low, undermining the assessment of hepatic conditions. Troponin, a cardiac biomarker, can yield inaccurate readings, affecting evaluations of myocardial injury. Additionally, the concentration of specific drugs within therapeutic monitoring might be underestimated due to hemolytic alterations, compromising treatment regimens. Such distortions highlight the necessity for methodological adjustments and heightened awareness of hemolysis impacts on test results to maintain diagnostic integrity.
Practical strategies labs use to reduce hemolysis impact
Best practices for sample collection, handling, and processing
Lab professionals employ strategic approaches to minimize hemolysis impacts, beginning with adherence to best practices in sample collection. Utilizing appropriately sized needles for venipuncture and ensuring precise technique minimizes cellular trauma. It is vital to avoid excessive force during blood draw and promote gentle mixing. Limiting transport time and ensuring samples remain at consistent, optimal temperatures further protect sample integrity. Additionally, standardizing protocols for equipment handling and leveraging advanced processing techniques help reduce hemolysis risk and enhance the reliability of test results.
Risk-reduction tools and bioanalytical tactics
Incorporating risk-reduction tools and bioanalytical strategies, such as those developed by WuXi AppTec, provides further means to counteract hemolysis impacts. Employing hemolysis assessment approaches during sample evaluation aids in identifying compromised specimens. Stability checks and matrix qualification further ensure an assay’s robustness against hemolytic interference. Complementary technologies and innovation in bioanalytical techniques continue to evolve, offering labs the capability to enhance the accuracy and reliability of analyses, delivering clearer, more actionable insights for clinicians.
Conclusion
Hemolysis in blood samples poses a significant challenge in achieving precise laboratory results. Its impact on analyte concentrations can distort diagnostic conclusions, emphasizing the necessity for rigorous protocols and awareness in sample handling and analysis. By understanding hemolysis and incorporating strategic practices and innovative tools, labs can effectively mitigate its effects, ensuring accurate, reliable diagnostic outputs. This holistic approach not only streamlines laboratory processes but bolsters the overall quality of healthcare delivery—underscoring that informed actions against hemolysis translate to enhanced patient care and outcomes.








