Why Is Immunogenicity Testing Essential for Biologics?
Immunogenicity testing helps developers understand how a patient’s immune system may react to a biologic therapy. These reactions can change drug exposure, reduce efficacy, or create safety risks. By evaluating immune responses early, teams make better development decisions and support safe clinical use. Strong immunogenicity strategies ensure biologics deliver consistent performance and meet regulatory expectations throughout their lifecycle.

Understanding Immunogenicity in Biologic Therapies
How the Immune System Reacts to Biologic Molecules
The immune system identifies biological molecules as foreign when structural features or impurities activate immune pathways. This recognition triggers antibody production, cytokine release, or cellular responses. These reactions vary in intensity and timing across patients. Understanding how biologics engage the immune system helps developers predict risks, design safer molecules, and refine testing plans that support reliable therapeutic performance.
Factors That Increase Immunogenicity Risk
Several factors raise immunogenicity risk, including molecular structure, aggregation, formulation components, and impurities. Administration route, dose frequency, and patient-specific conditions also shape immune responses. Manufacturing changes may alter product attributes and influence risk levels. Identifying these factors early allows teams to adjust development strategies, strengthen quality control, and reduce the likelihood of unwanted immune reactions during clinical use.
Consequences of Uncontrolled Immune Responses
Uncontrolled immune responses can neutralize the biologic, reduce therapeutic effect, or trigger hypersensitivity reactions. Some antibodies accelerate clearance, lowering drug exposure. Severe cases may cause adverse events that limit treatment options. Understanding these consequences helps developers prioritize immunogenicity studies and develop mitigation strategies. Early insight protects patient safety and improves the reliability of biologic therapies across long-term treatment.
The Role of Immunogenicity Testing in Drug Development
Detecting and Characterizing Anti-Drug Antibodies
Immunogenicity testing identifies anti-drug antibodies that form in response to biologic therapies. These tests detect early immune activation and track antibody class, affinity, and persistence. Characterizing these responses helps developers understand whether antibodies neutralize the drug or alter exposure. Accurate detection supports clinical decision-making and strengthens evidence for safety and efficacy throughout development.
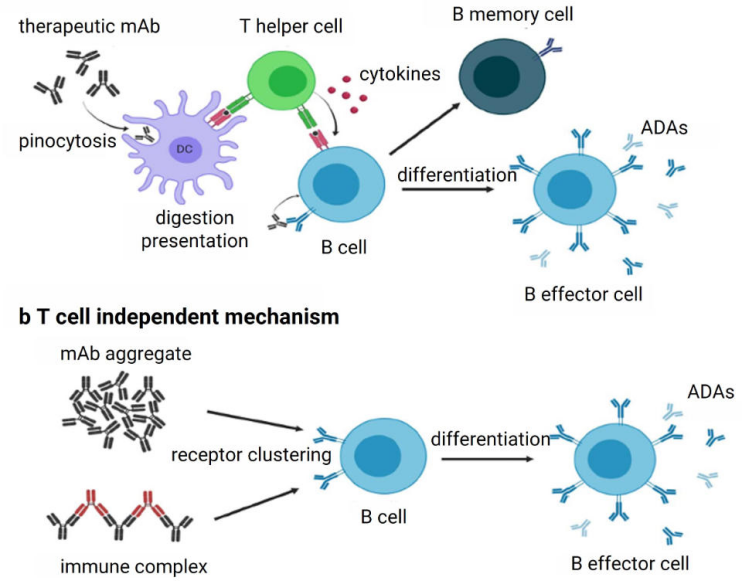
Assessing Impact on Drug Safety and Efficacy
Anti-drug antibodies may reduce a biologic’s effectiveness or cause adverse reactions. Immunogenicity testing helps determine whether immune responses change PK profiles, increase clearance, or trigger hypersensitivity. By linking antibody levels with clinical outcomes, teams understand how immunogenicity affects real-world performance. This insight guides risk management and ensures patients receive safe, effective, and predictable treatment across therapy cycles.
Supporting Dose Selection and Treatment Planning
Understanding immune responses helps developers refine dose levels, adjust intervals, and plan long-term treatment strategies. When immunogenicity affects exposure, PK and ADA data guide appropriate adjustments. By integrating immunogenicity insights into clinical planning, teams reduce variability and improve therapeutic consistency. This approach ensures patients receive dosing that accounts for immune responses and maintains biologic effectiveness.
Key Methods Used in Immunogenicity Evaluation
Screening Assays for Early Antibody Detection
Screening assays detect early signs of anti-drug antibodies with high sensitivity. Techniques such as bridging ELISA, electrochemiluminescence, or ligand-binding assays capture a broad range of antibody types. These early screens flag potential immune responses before they affect clinical outcomes. Effective screening ensures timely follow-up testing and supports comprehensive immunogenicity monitoring throughout development.
Confirmatory and Neutralizing Antibody Tests
Confirmatory assays verify whether detected antibodies truly target the biologic. Neutralizing antibody tests identify antibodies that block drug activity, affecting the therapeutic effect. These evaluations clarify the clinical relevance of immune responses and help predict performance issues. By distinguishing neutralizing from non-neutralizing antibodies, developers make informed decisions about safety, dosing, and long-term treatment planning.
Strategies to Manage Assay Interference Challenges
Immunogenicity assays face interference from drug levels, matrix effects, and endogenous antibodies. Effective strategies include acid dissociation, assay bridging formats, and drug-tolerant workflows. These approaches improve sensitivity and reduce false negatives. Managing interference ensures data accuracy and supports consistent detection. Strong assay design helps teams capture reliable antibody information across varied clinical samples and timepoints.
Regulatory Expectations for Biologic Immunogenicity
International Guidelines for Antibody Assessment
Regulators such as the FDA, EMA, and ICH require thorough immunogenicity testing for biologics. Guidelines outline assay validation, ADA characterization, neutralizing studies, and safety monitoring. Compliance ensures consistent evaluation across clinical phases. Understanding international expectations helps developers design programs that satisfy global regulatory standards and support smooth approval processes for new biologic therapies.
Reporting Requirements During Clinical Development
Regulatory agencies expect detailed reporting of immunogenicity data throughout clinical trials. Reports include assay methods, ADA incidence, neutralizing profiles, and correlations with safety or efficacy outcomes. Clear documentation supports transparency and helps reviewers assess risk. Accurate reporting ensures developers demonstrate how immunogenicity influences drug performance and how they manage potential safety concerns across trial phases.
Ensuring Long-Term Safety Through Follow-Up Testing
Long-term immunogenicity monitoring helps detect late-onset or persistent antibody responses. Follow-up testing assesses how immune reactions evolve over extended treatment. Regulators expect ongoing evaluation to ensure sustained safety and effectiveness. This monitoring supports lifecycle management and helps identify risks that may influence dosing, formulation, or patient selection for biologic therapies.
Conclusion
Immunogenicity testing is essential for biologics because it reveals how immune responses affect safety, exposure, and therapeutic effect. When developers evaluate antibodies early and throughout clinical phases, they reduce risk and improve treatment consistency. Strong testing strategies support regulatory success and guide dose planning. With reliable immunogenicity data and a clear understanding of immunogenicity define, teams deliver biologics that offer safer, more predictable outcomes for patients.








